The 13 Colonies: A Basis For A Nation
The 13 Colonies: A Basis for a Nation
Associated Articles: The 13 Colonies: A Basis for a Nation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to The 13 Colonies: A Basis for a Nation. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The 13 Colonies: A Basis for a Nation

The 13 unique colonies, a bunch of British settlements alongside the Atlantic coast of North America, performed a pivotal position within the formation of america of America. Their distinctive historic, geographical, and social traits contributed to the event of a definite American identification and laid the groundwork for the nation’s future.
A Visible Journey By Historical past
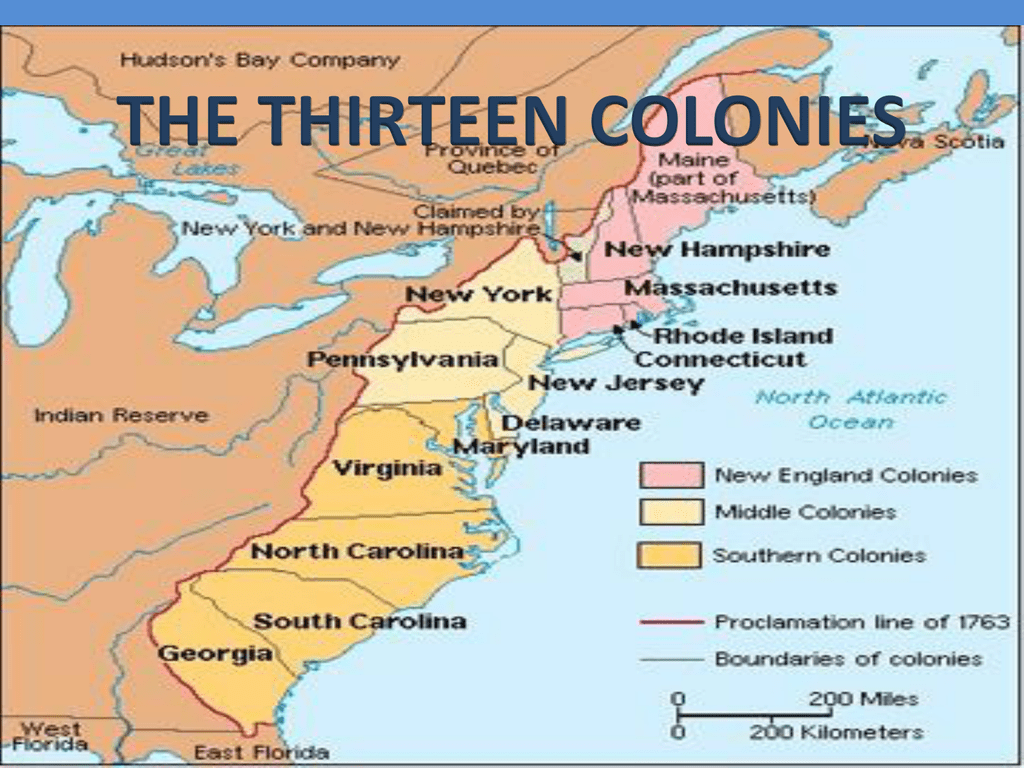
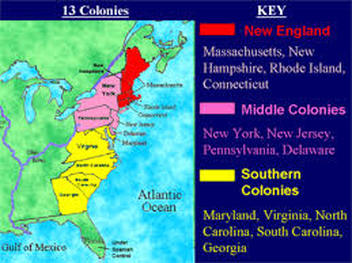
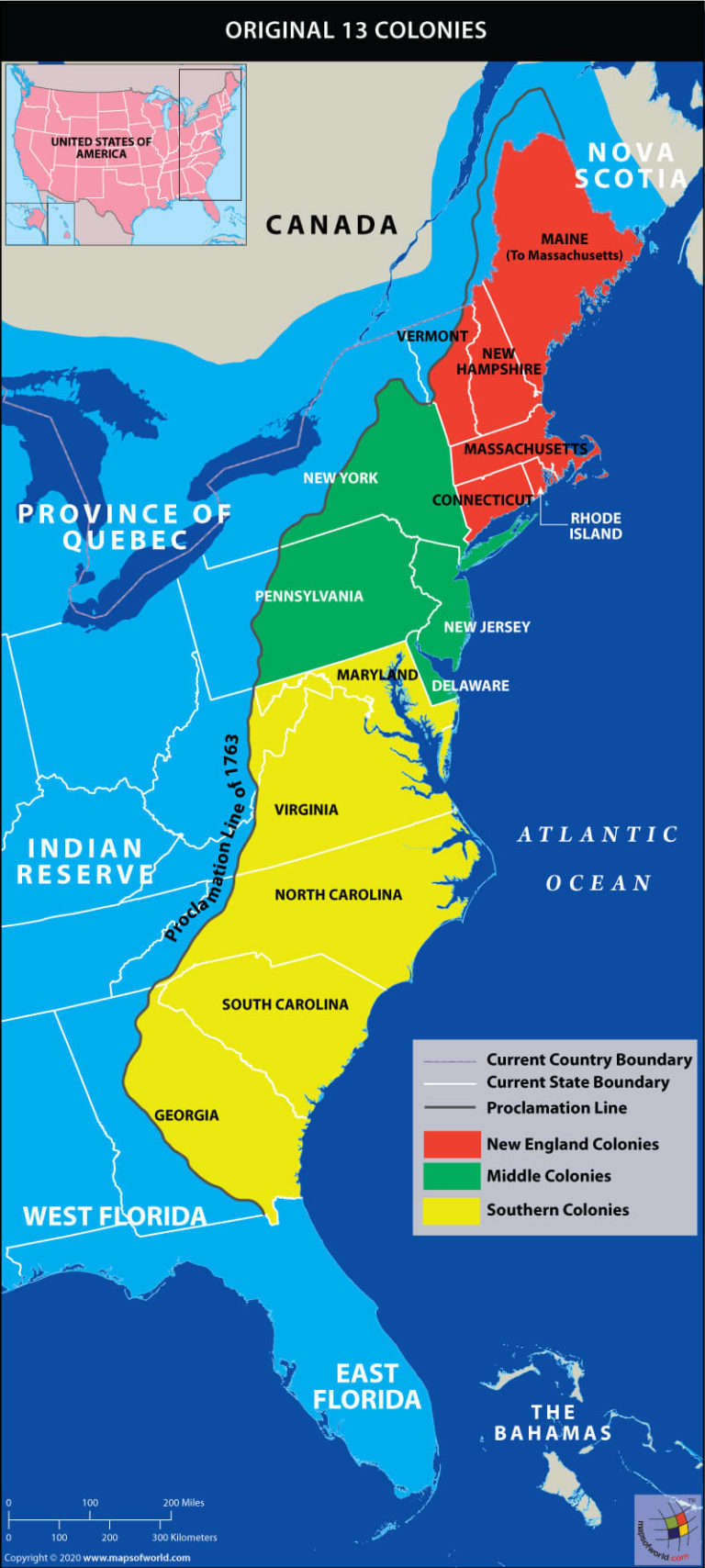
Map of the 13 Colonies:
[Insert a map of the thirteen colonies here, clearly labeling each colony and its borders.]
Exploring the 13 Colonies
1. New Hampshire (1623): Located within the northernmost area, New Hampshire was based by English settlers in search of non secular freedom and financial alternatives. Its rugged terrain and ample forests fostered a robust timber business and a tradition of self-reliance.
2. Massachusetts (1620): The guts of early Puritan settlement, Massachusetts was identified for its robust non secular affect, its dedication to training, and its thriving fishing and shipbuilding industries. The colony’s mental and spiritual fervor performed a vital position in shaping American values.
3. Rhode Island (1636): Based by Roger Williams, who championed non secular tolerance and separation of church and state, Rhode Island grew to become a haven for these in search of freedom from non secular persecution. It developed a robust maritime custom and have become a middle for commerce.
4. Connecticut (1636): With its fertile lands and entry to the Connecticut River, Connecticut attracted settlers in search of agricultural prosperity. The colony’s robust sense of self-governance and its early adoption of consultant authorities set a precedent for American democracy.
5. New York (1624): Initially established by the Dutch as New Netherland, New York was captured by the English in 1664 and renamed after the Duke of York. Its strategic location on the Hudson River made it an important buying and selling hub and a middle for immigration.
6. New Jersey (1664): Located between New York and Pennsylvania, New Jersey provided fertile land and a various inhabitants, attracting farmers, retailers, and artisans. Its non secular tolerance and its dedication to training contributed to its cultural richness.
7. Pennsylvania (1681): Based by William Penn, a Quaker who believed in non secular freedom and peaceable coexistence, Pennsylvania grew to become a haven for various non secular teams. Its fertile lands attracted farmers, and its dedication to training and tolerance fostered a thriving mental tradition.
8. Delaware (1638): Initially a part of Pennsylvania, Delaware grew to become a separate colony in 1701. Its location on the Delaware River made it a strategic buying and selling heart, and its agricultural financial system offered a robust basis for its development.
9. Maryland (1632): Established by Lord Baltimore as a haven for Catholics, Maryland grew to become a various colony with a robust agricultural financial system. Its tolerance for various religions and its dedication to self-governance set a precedent for American non secular freedom.
10. Virginia (1607): The primary everlasting English settlement in North America, Virginia was based primarily for financial causes. Its tobacco plantations, based mostly on the labor of indentured servants and enslaved Africans, fueled the colony’s financial development and contributed to the event of a definite Southern tradition.
11. North Carolina (1653): Recognized for its fertile lands and its ample timber sources, North Carolina attracted settlers in search of agricultural alternatives and a extra unbiased life-style. Its various inhabitants and its robust sense of native autonomy performed a major position in shaping its identification.
12. South Carolina (1663): Based as a haven for English settlers in search of financial alternatives, South Carolina developed a robust agricultural financial system based mostly on rice and indigo plantations. Its reliance on enslaved labor and its shut ties to the British West Indies formed its social and financial panorama.
13. Georgia (1732): Established as a buffer colony between British settlements and Spanish Florida, Georgia was based with the intention of selling social reform and financial improvement. Its various inhabitants, together with debtors in search of a recent begin and settlers in search of financial alternatives, contributed to its distinctive character.
The Legacy of the 13 Colonies
The 13 colonies performed a pivotal position within the improvement of america. Their experiences with British rule, their struggles for self-governance, and their various social and financial buildings formed the nation’s political, social, and cultural panorama. The American Revolution, a struggle for independence from British rule, was sparked by the colonies’ rising resentment in the direction of British insurance policies and their need for higher autonomy.
The success of the American Revolution and the next institution of america as an unbiased nation solidified the 13 colonies’ place in American historical past. Their legacy continues to resonate within the nation’s political system, its cultural identification, and its dedication to freedom and self-governance.
FAQs
1. What have been the principle causes for the founding of the 13 colonies?
The 13 colonies have been based for a wide range of causes, together with non secular freedom, financial alternative, political asylum, and strategic geopolitical issues. Some colonies, like Massachusetts and Pennsylvania, have been established by non secular teams in search of refuge from persecution, whereas others, like Virginia and South Carolina, have been based by people in search of financial achieve by means of land possession and commerce.
2. What have been the key variations between the northern and southern colonies?
The northern and southern colonies developed distinct social, financial, and cultural traits. The northern colonies, with their colder local weather and rocky terrain, targeted on fishing, shipbuilding, and commerce. Additionally they had a extra various inhabitants, together with immigrants from varied European nations. The southern colonies, with their hotter local weather and fertile lands, developed an agricultural financial system based mostly on plantation crops like tobacco, rice, and indigo. They relied closely on enslaved labor and had a extra homogeneous inhabitants.
3. What position did the 13 colonies play within the American Revolution?
The 13 colonies performed a pivotal position within the American Revolution. Their rising resentment in the direction of British insurance policies, together with taxation with out illustration and restrictions on commerce, fueled the motion for independence. The colonists organized militias, fought towards British forces, and finally succeeded in securing their independence by means of a collection of decisive battles.
4. What have been the key challenges confronted by the 13 colonies?
The 13 colonies confronted a wide range of challenges, together with conflicts with Native Individuals, financial instability, and political disagreements. Additionally they struggled with points like slavery, non secular intolerance, and social inequality. These challenges contributed to the event of a definite American identification and formed the nation’s political and social panorama.
5. How did the 13 colonies contribute to the event of america?
The 13 colonies laid the muse for america as a nation. Their experiences with British rule, their struggles for self-governance, and their various social and financial buildings formed the nation’s political, social, and cultural panorama. Their legacy continues to resonate within the nation’s political system, its cultural identification, and its dedication to freedom and self-governance.
Suggestions for Finding out the 13 Colonies
- Use major sources: Discover historic paperwork, letters, diaries, and different firsthand accounts to achieve a deeper understanding of life within the 13 colonies.
- Concentrate on the person colonies: Every colony had its personal distinctive historical past, tradition, and challenges.
- Join the colonies to broader historic themes: The 13 colonies have been a part of bigger historic actions, together with the Age of Exploration, the Atlantic slave commerce, and the Enlightenment.
- Take into account the views of various teams: Discover the experiences of Native Individuals, enslaved Africans, ladies, and different marginalized teams to achieve a extra nuanced understanding of colonial life.
- Use maps and visible aids: Maps, charts, and timelines will help you visualize the geographical and chronological context of the 13 colonies.
Conclusion
The 13 unique colonies performed a vital position within the formation of america of America. Their distinctive historic, geographical, and social traits contributed to the event of a definite American identification and laid the groundwork for the nation’s future. By finding out the 13 colonies, we achieve a deeper understanding of the origins of america, its core values, and its enduring legacy.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into The 13 Colonies: A Basis for a Nation. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!